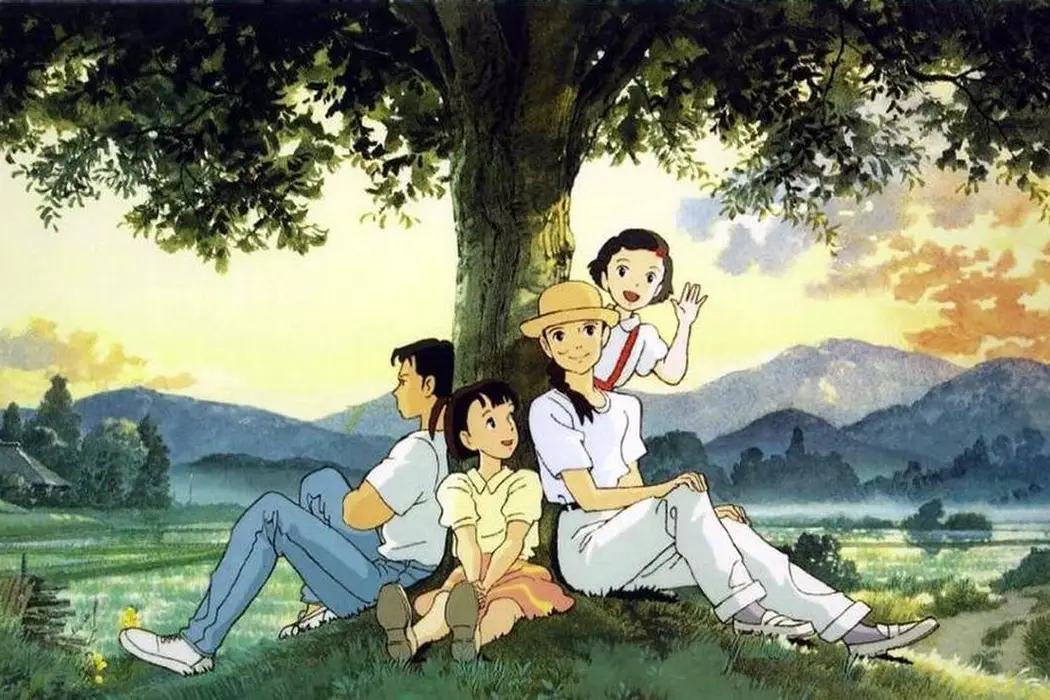
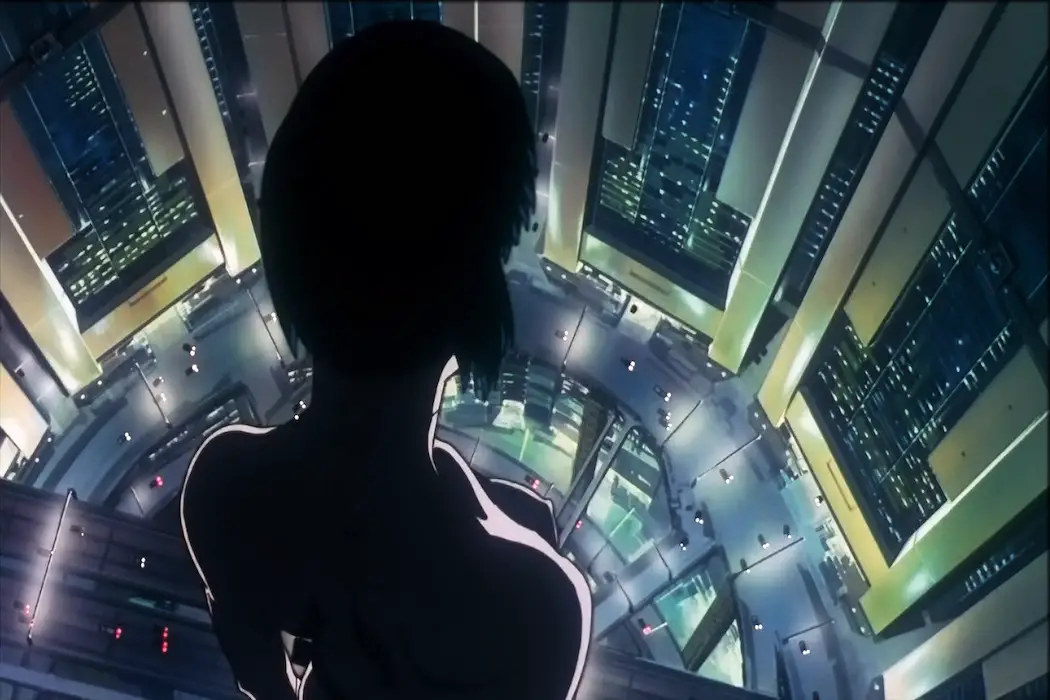
Japan
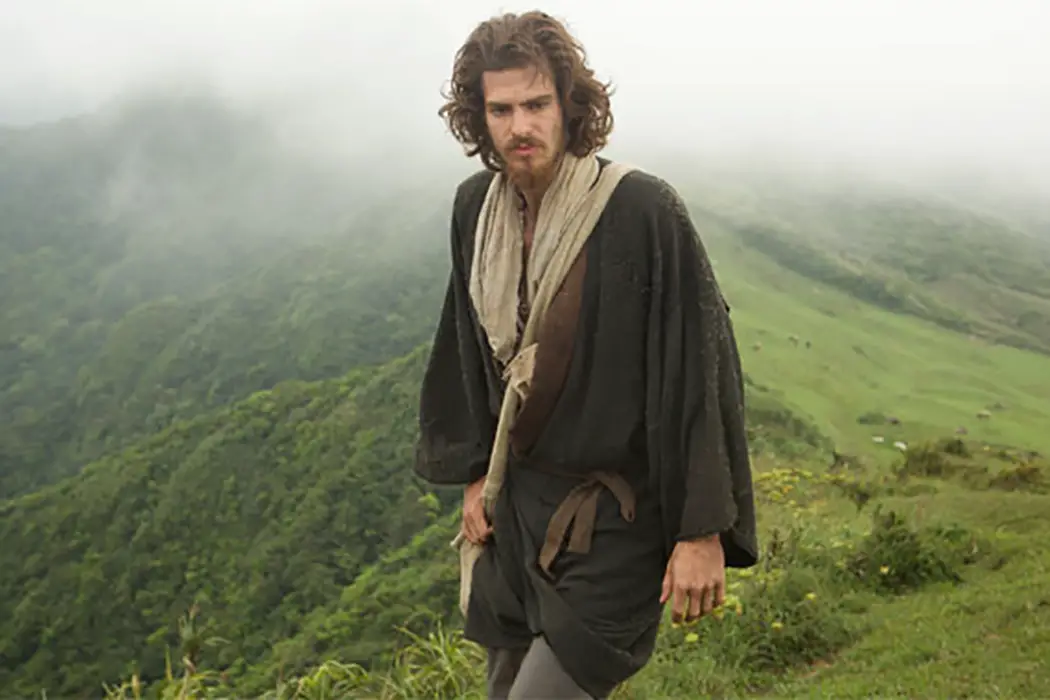

Martin Scorsese’s Silence begins with a dark, blank screen, with only the gentle humming of cicadas heard on all sides. It then immediately opens up to an overcast shot overlooking the banks of a river, where numerous people are being strung up and tortured. Such a peaceful moment undercut by extreme violence is very much an indication of what’s to come.
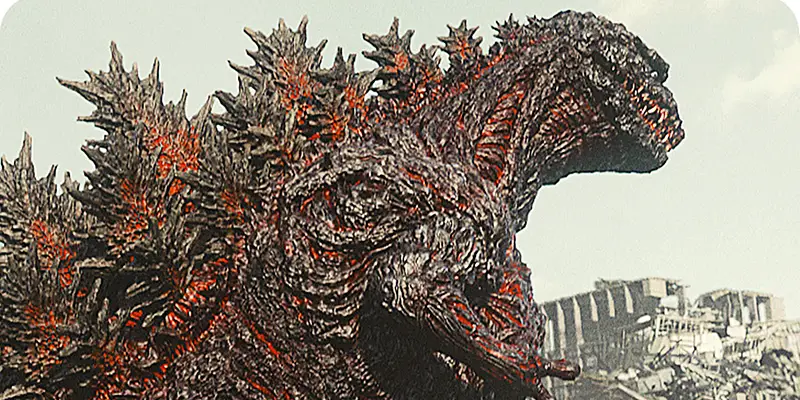

The Godzilla franchise has had a long and storied history, dating back to the original motion picture of 1954 directed by Ishirō Honda. Produced and distributed by famed Japanese film studio Toho, the original feature has spawned multiple franchise sequels over the years, from both its country of origin and the United States. Starting with the 1956 Japanese-American remake of Honda’s original feature from only two years prior, Godzilla, King of the Monsters!

Film is one of the best artistic mediums because it’s always growing; it speaks every language, and every place in the world has their iteration as to what’s scary, twisted, weird or just downright bizarre. Different countries offer different interpretations of horror, from China where vampires hop to Korean Shaman. They don’t wave crosses, nor do they compel the power of Christ upon anyone, but just don’t fall in love with Isabelle Adjani.
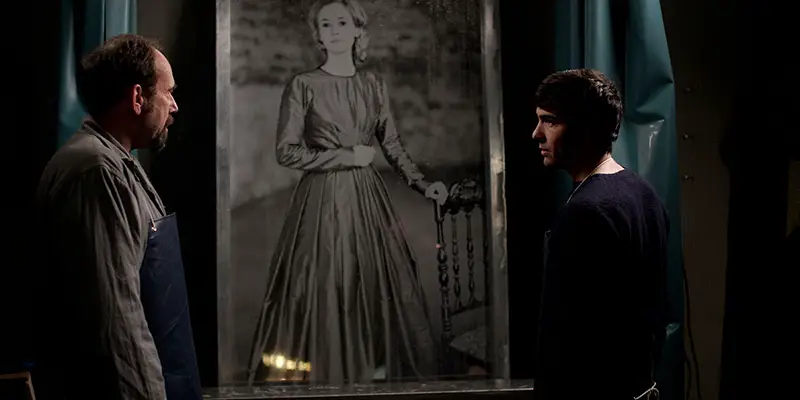

When the title card appears in Daguerrotype, it announces the film as “Le secret de le chambre noire”. That title reflects the film’s goals as a dark, foreboding ghost mystery, and it probably does so better than the title “Daguerrotype” does. But what I like about the title Daguerrotype (misspelled though it might be), is that it refers to the most interesting part of the film:
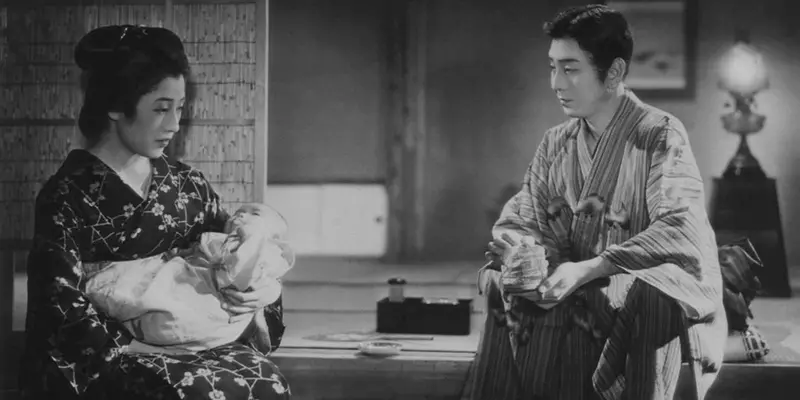

Kenji Mizoguchi’s The Story of the Last Chrysanthemum follows Kikunosuke and Otoku, a young couple in late 19th Century Japan. Kikunosuke is the adopted son of a famous kabuki house, and an emerging kabuki actor; Otoku is one of his family’s servants. Most people, including his adopted father, think Kikunosuke is no good as an actor, but they only criticize him behind his back.
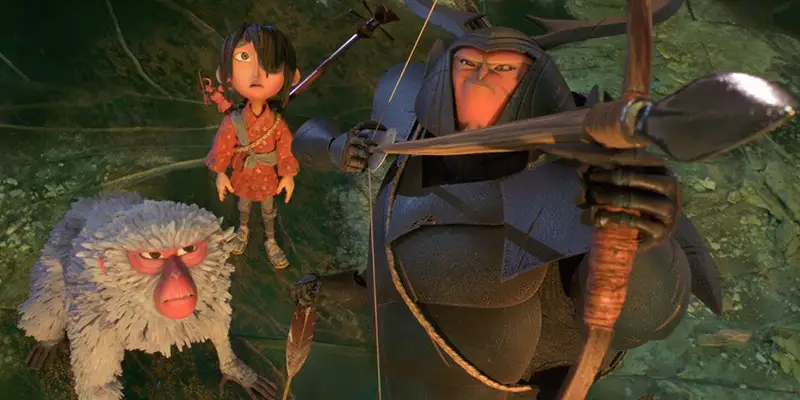

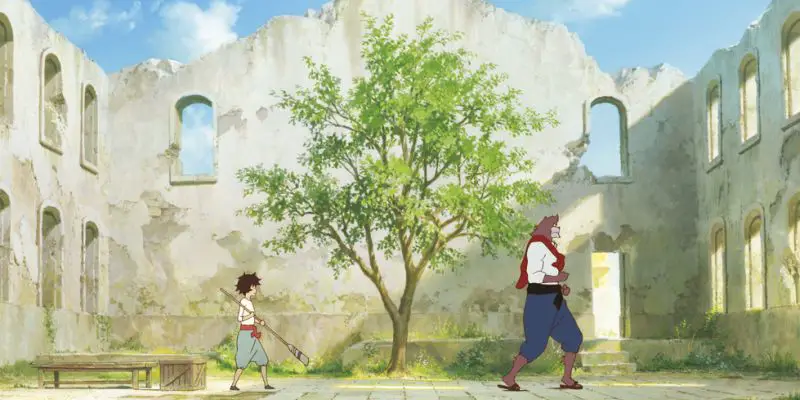
Kubo and the Two Strings is a genuine masterpiece. The word “masterpiece” might be used carelessly and far too often these days when discussing contemporary movies. At the least, Kubo has fulfilled the conventional definition of “masterpiece” no matter how semantically satiated the word has become, if not entirely forging a new meaning altogether.

Among the animation giants of Disney and DreamWorks, it’s good to recognize directors who have perfected their craft outside the western sphere, and we’re not talking Hayao Miyazaki here (although he’s but a stone’s throw away). Satoshi Kon is a Japanese anime director known for his blending of fantasy and reality in his slickly edited films. In contrast to the magical animated realities of Studio Ghibli, Kon’s realities are completely grounded in the modern era, their subject matter rooted in the intertwining of identity and technology.