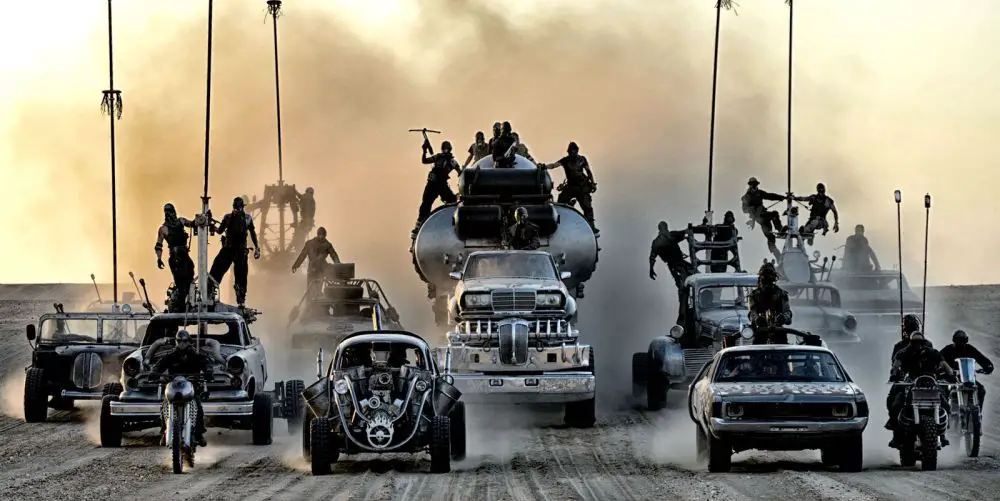
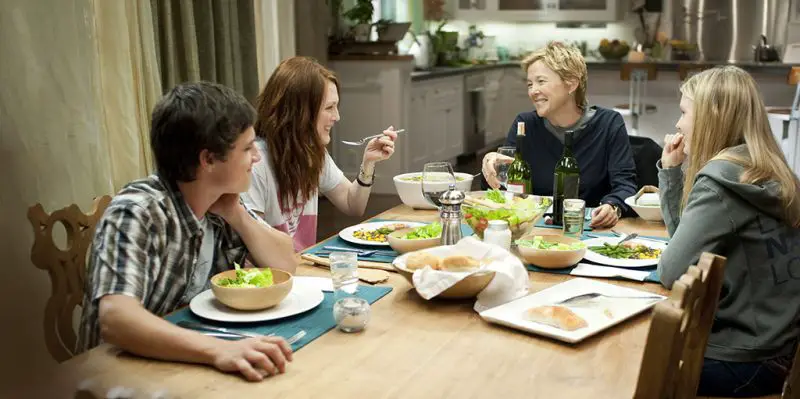film analysis
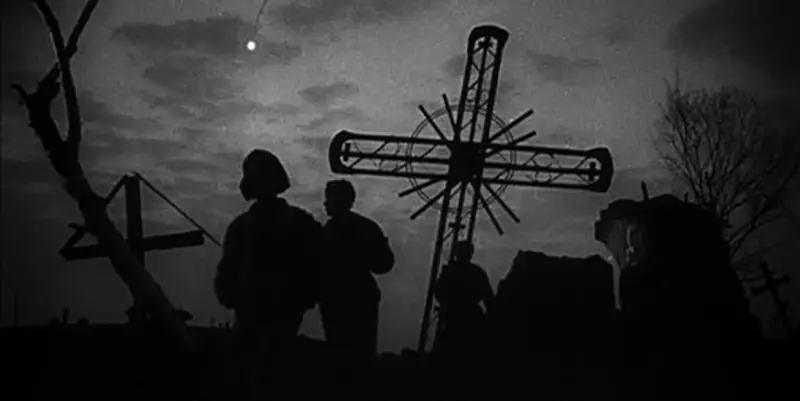

About midway through Andrei Tarkovsky’s feature 1962 film debut of Ivan’s Childhood, in the midst of a Russian battlefield field torn asunder during World II, a cross is backlit by a setting sun. The cross is obscured in shadow and yet its beauty remains. A spiritual man, Tarkovsky was never afraid to ask questions about spiritual matters.

Class consciousnes and its oft-contingent condemnation of wealth was a theme at the 2016 Cannes Film Festival that one would be hard-pressed to overlook. The most obvious reason for this is the fact that Ken Loach’s poignant portrait of one man’s struggle to navigate Britain’s welfare system, I, Daniel Blake, took home the Palme d’Or. But this topic was also prominent in part because films about wealth, or lack thereof, pervaded the entire festival, spanning its various sections.
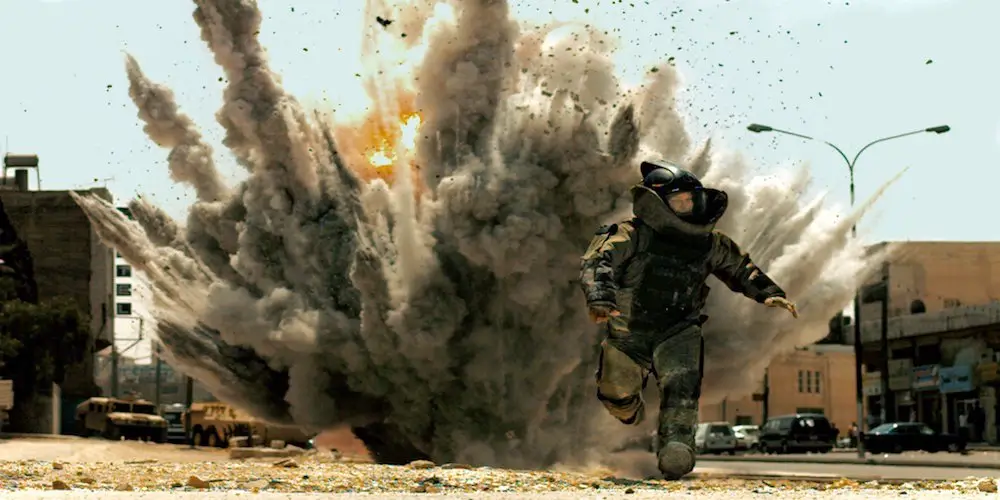

One of the most overlooked elements of the action genre is sound – more specifically, its use of sound cues to tell a story. However, this mode of storytelling is not only powerful by itself, but is especially suited to the needs of modern action films. Recent advances in sound technology now make it possible for action directors to put sound cues to their full use.
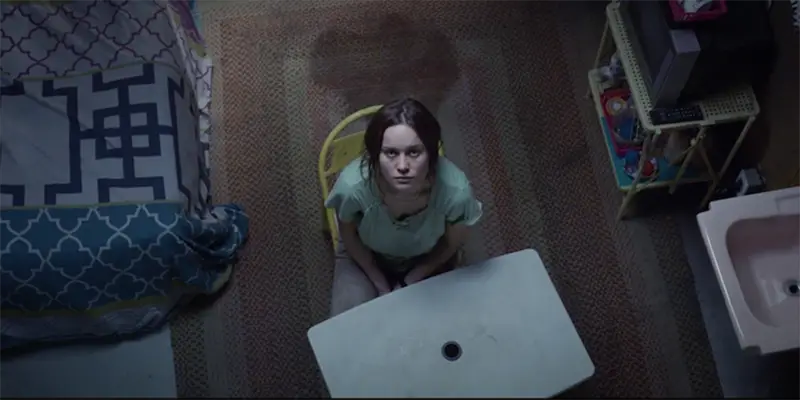
Because the Internet can take a person virtually anywhere in the world and provide potentially infinite vats of knowledge, raising children in a dictatorial environment nowadays seems more ridiculous than ever. The mechanics of detaining an adult with an existing awareness of the outside world is even more bewildering, because chances are they’ve read about the Josef Fritzl case and have at least some idea of how to escape. Alas, cinema, ever the portrayer of such cultural terrors, has provided startling means with which to explore such a phenomenon.
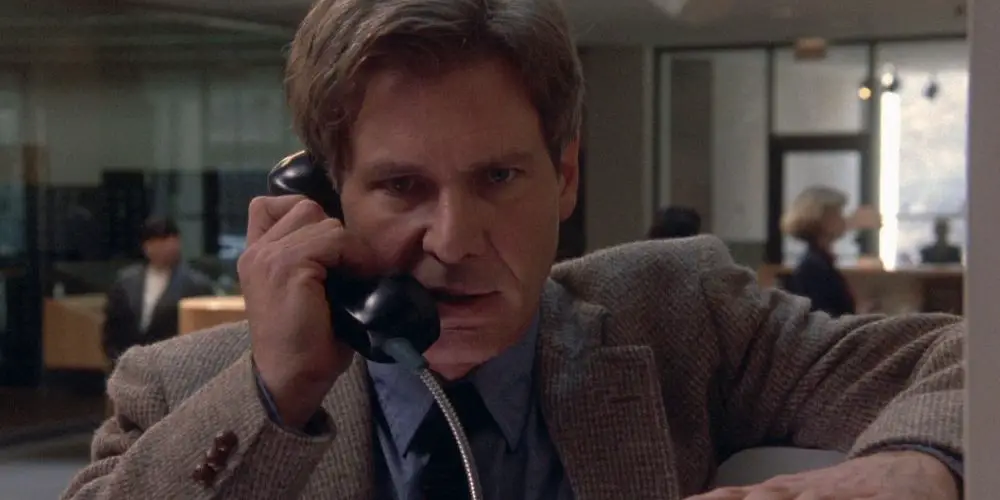

In Andrew Davis’ brilliant 1993 thriller The Fugitive, the filmmakers use a variety of techniques to lead the viewer through the story. They drop hints with color and lighting that viewers are not necessarily trained to consciously notice while they’re watching, and employ a gripping editing style that effectively supports the cat-and-mouse game that embroils the film’s two main characters. Every movie has content, which is what is seen and heard on screen, and what is referred to as form, which is the way in which the film’s creators manipulate that content to their own ends and present it to the viewer.
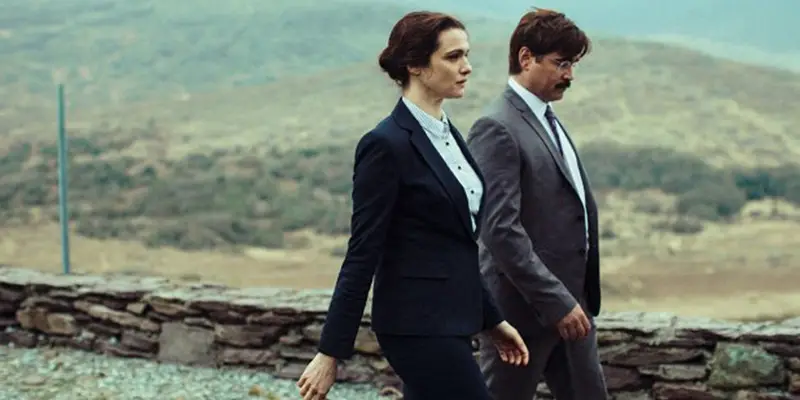

Director Yorgo Lanthimos first grabbed the world’s attention with Alps and the seismic Dogtooth. Recently, he sprung another biting, absurdist satire into the festival circuit with The Lobster. It takes place in a world in which relationships are mandatory; the characters, all newly single, or newly of age, are detained in a hotel that works, basically, as a deadly speed dating service.
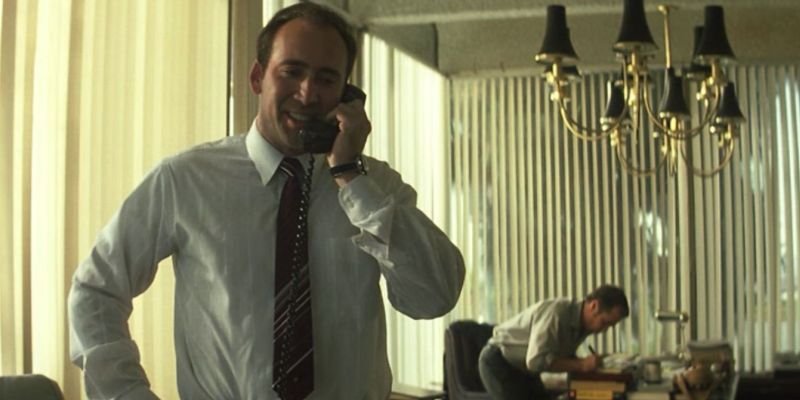

Whenever I watch a Nicholas Cage movie I feel myself expecting to see a certain eccentricity in his performance. His over the top outbursts or erratic body movements distance away from more serious tones and instead cross over into that of slapstick comedy. Cage’s acting has always entertained me, yet my ironic enjoyment often makes it hard to take his characters seriously.
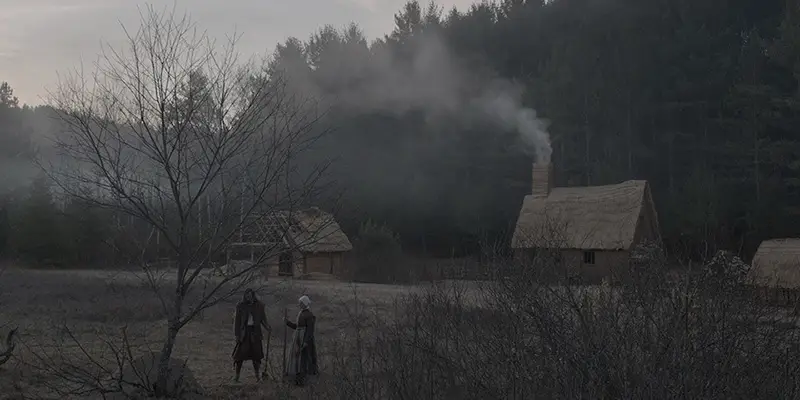

Set in 1630, Robert Eggers’ The Witch follows a family banished from a Puritan community and forced to live, isolated and penniless, in a remote woodlands shack. Soon, malevolent forces begin to molest the kids and infect the goat, and the family is engulfed in a maelstrom of religious hysteria and occultist magic. With its deeply unsettling atmosphere and frenzied performances, The Witch has (not undeservedly) become one of the most acclaimed horror films of the new millennium, with many critics praising its attention to detail and the slow-burning tension of its narrative (as well as its mascot:

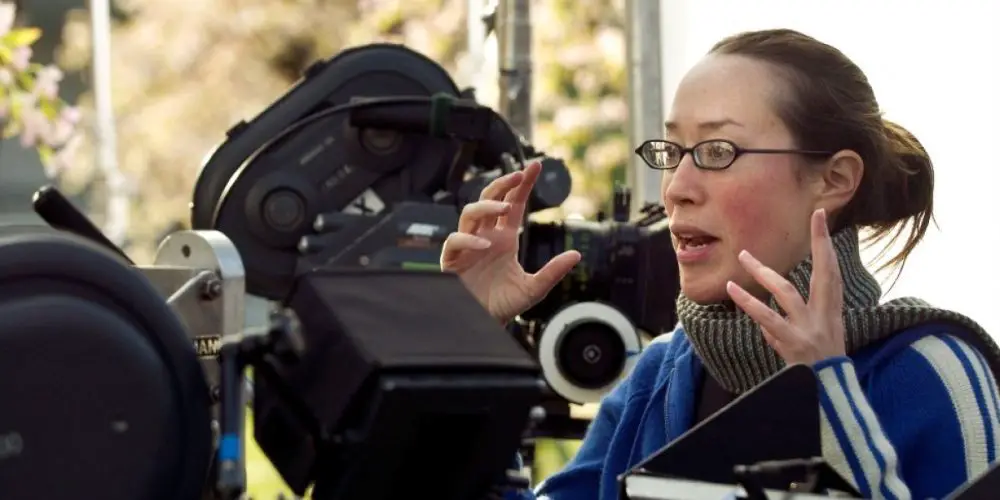
In this third episode of The Power of Film, I spoke with the lovely Samantha Shada. She is a director, hosts the screening series Seeking Our Story, and she works at one of the big studios – a busy lady who has a lot of unique insights into the world of film! We spoke about a lot, from film in general and symbolism in film, the status quo of the studio system (and, very interesting, the current state of film marketing) to film preservation.