Features
Because the Internet can take a person virtually anywhere in the world and provide potentially infinite vats of knowledge, raising children in a dictatorial environment nowadays seems more ridiculous than ever. The mechanics of detaining an adult with an existing awareness of the outside world is even more bewildering, because chances are they’ve read about the Josef Fritzl case and have at least some idea of how to escape. Alas, cinema, ever the portrayer of such cultural terrors, has provided startling means with which to explore such a phenomenon.
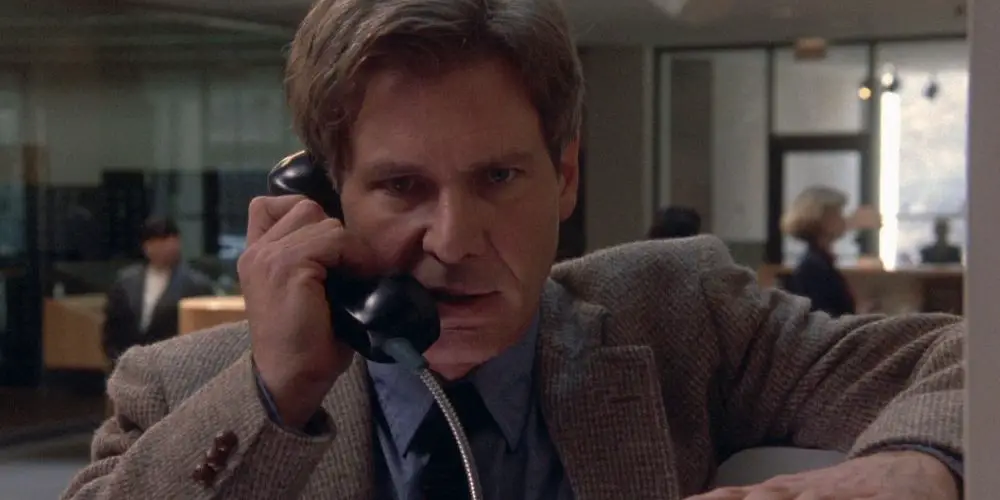

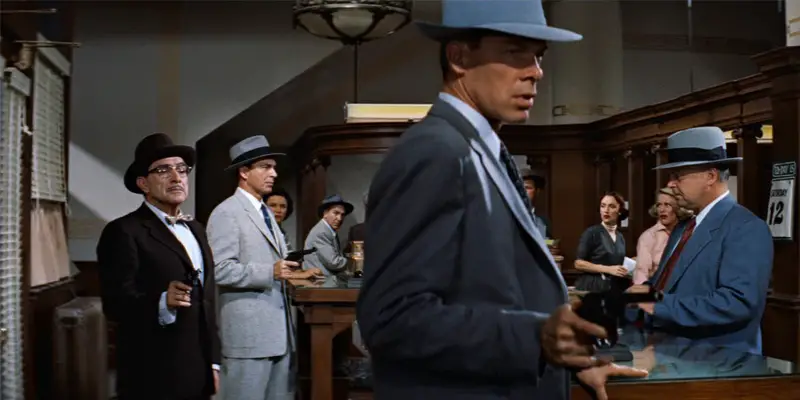
In Andrew Davis’ brilliant 1993 thriller The Fugitive, the filmmakers use a variety of techniques to lead the viewer through the story. They drop hints with color and lighting that viewers are not necessarily trained to consciously notice while they’re watching, and employ a gripping editing style that effectively supports the cat-and-mouse game that embroils the film’s two main characters. Every movie has content, which is what is seen and heard on screen, and what is referred to as form, which is the way in which the film’s creators manipulate that content to their own ends and present it to the viewer.
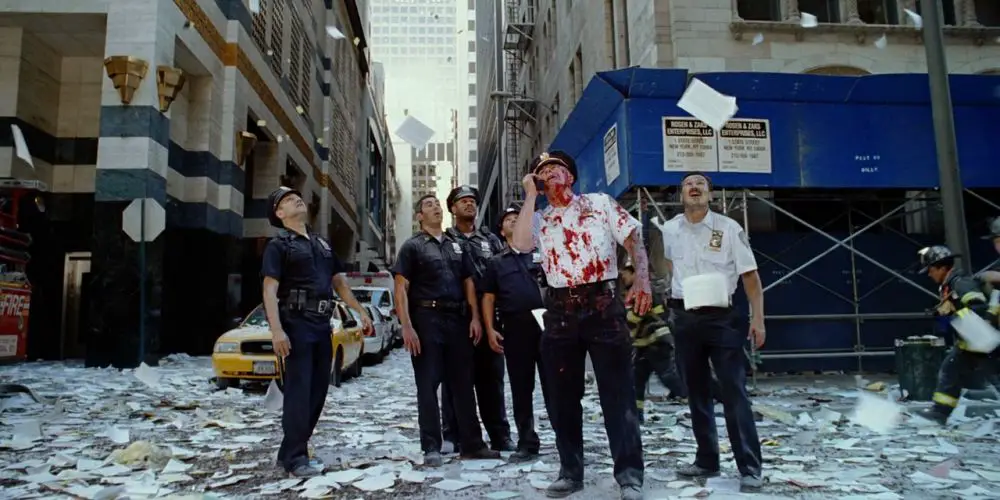

Recently, I had the chance to tour the National 9/11 Memorial and Museum in New York City, which, as you can imagine, is quite a somber experience. Amid the thoughtfully presented exhibits, I started wondering about 9/11 as portrayed in film. Now, when I say “portrayed” I’m not talking tangentially, as when 9/11 is used to jumpstart plot (e.

We have all watched a globetrotter movie at some point and thought “man, I want to do that!” Regardless of if you’re an avid adventurer or a couch potato, film can ignite that urge for discovery and make audiences want to grab life by the horns. Whilst most wanderlust movies satisfy a craving for exploration, I have realised that only a select few have the power to truly motivate viewers, making them want to escape their lives of comfort and luxury and replace it with blisters and exhaustion.

Let me know if you’ve heard this one. A man wakes up after an accident with no memory of who he is or where he’s been, and while incredibly disabling, his predicament leads him down a lengthy search to discover his past and identity. This and other uses of memory loss have been popular in film for generations.

As a society, recent events have left us more divided than ever. The people on one side of this socio-political argument are trying to undermine unrepresented voices in the culture by calling for a cry back to the “good old days” and using hateful rhetoric in order to get what they want. The other side are being labelled as mere “liberals” with a politically correct agenda that isn’t attuned to the desires of the majority of people.
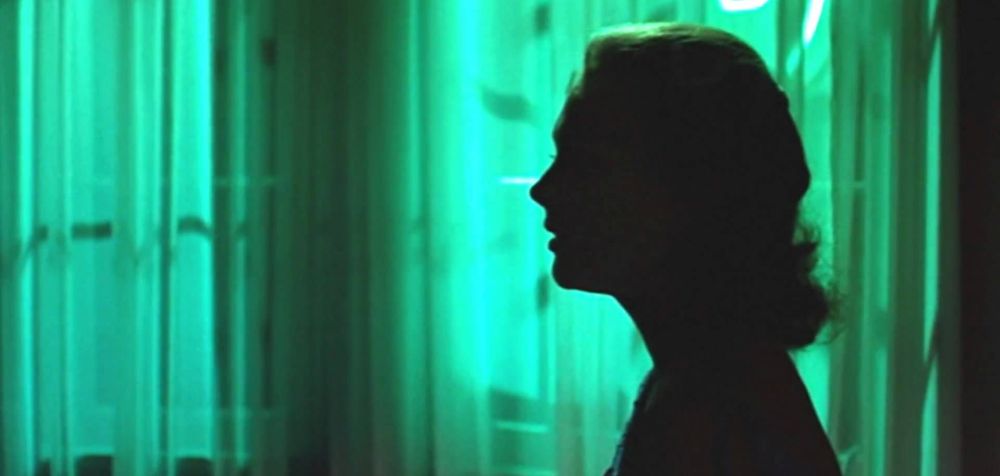

Sexism in film has been a topic of discussion since the rise of feminism, and in particular, since Laura Mulvey’s 1970’s research into ‘the male gaze’ in cinema. Fortunately, modern films are slowly but surely making a conscious effort to break down stereotypical gender roles and tired one-dimensional characters, but when it comes to the classics, many of the limited and restricted archetypes we try to move away from today are showcased in these films. This year, Alfred Hitchc*ck’s mystery thriller Vertigo was voted the greatest film of all time by a BFI poll.









